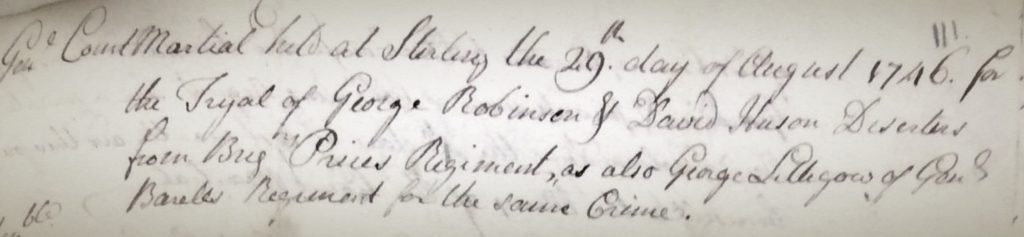Amidst the complexities of dynastic opposition and civil war during the later Jacobite era, the loyalties and material commitment of individuals were often in flux and have not always been so simple for historians to cleanly define. Allegations of significant Jacobite desertions have long been suspected (and more recently have been examined), but little scholarly enquiry has been made into cases of defection by soldiers within the government forces who were charged with quelling the Jacobite threat in Britain during the ’45.1 Resistance to martial service permeated both sides of the conflict, but deserting ranks to avoid combat is one thing, while joining up with the enemy is another entirely. Archival evidence shows us that soldiers in British service – including loyalist Highlanders on campaign in Scotland – deserted their units in smaller numbers than their Jacobite rivals, but incidents of soldiers breaking ranks was still a problematic issue for British army officers and Hanoverian officials.2 Digging deeper into the sources further reveals that some of these deserters found both cause and motivation to fight amidst the ranks of Jacobite rebels.
Category: Policies (page 1 of 3)
The collective social power and reach of the parish minsters in the Presbyterian Church of Scotland was one of the British government’s most potent weapons in quelling the last Jacobite rising.3 These ministers, in addition to being sanctioned recipients for the submission of illegal arms and an integral part of the extensive information network employed to identify alleged rebels, were some of the only people in Scotland that some prominent members of the military felt they could trust.4 Alexander Melville, 5th Earl of Leven, who was High Commissioner of the General Assembly during the Forty-five, remarked to Thomas Pelham-Holles, 1st Duke of Newcastle and Secretary of State, at the end of May 1746 that the loyalty of the Scots clergy was exemplary, and despite ‘the smooth arts of flattery & cajoling’ used by the Jacobites to gain their trust, only two specific ministers were known to have any sensitivities to the cause.5
To effectively quell the martial threat of the last Jacobite rising in 1745-6, Hanoverian government officials and British military personnel worked together to wage a systematic campaign of disarmament, capture, and prosecution against a mercurial enemy. Their goal, of course, was to identify and punish the most notorious and active rebels for sedition and high treason against the Crown. But it quickly became apparent that there was no possibility enough prison space could be requisitioned to hold the sheer number of alleged Jacobites, both soldiers and civilians, who were brought in upon suspicion or in active rebellion during the nine months of the conflict. British gaol keepers were similarly beleaguered in the aftermath of the 1715 Rising, when as many as 2000 prisoners needed space and subsistence while the process of prosecution played out. In 1745-6, the Jacobite army was significantly smaller, yet well over 3500 suspected persons were immured within a prison system that had not been notably improved or expanded in the preceding thirty years.6
Welcome to the research blog of JDB1745! Feel free to join in the conversation or contact us with any thoughts or questions you might have.

Tags
Tweets
The new collection edited by @LeithDavis & Kevin James is now up for pre-order, and it's 30% off with the code NEW30 at @EdinburghUP. My chapter on #Jacobite witness networks appears alongside a wonderful collection of esteemed historians and scholars.
https://edinburghuniversitypress.com/book-shaping-jacobitism-1688-to-the-present.html
Volunteers have found impacted musket balls where government forces engaged the Jacobite army 278 years ago at Blàr Chùil Lodair (the Battle of Culloden) ⚔️
Serving personnel and others are helping @NTS_archaeology uncover buttons, coins and more at the Highland battlefield.
Archaeologists are hoping techniques used during the excavation of Waterloo can help uncover new secrets at #Culloden Battlefield. A new dig at the site of the final clash of the #Jacobite Rising in 1746 is being led by @N_T_S. https://shorturl.at/Mdiyb
About
Little Rebellions is the official research blog for the Jacobite Database of 1745 project. Within it, we explore archival case studies, share technical notes and features, and contribute to the field of Jacobite studies with news, articles, and event announcements within and across the discipline.
© 2026 Little Rebellions
Modified Hemingway theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑