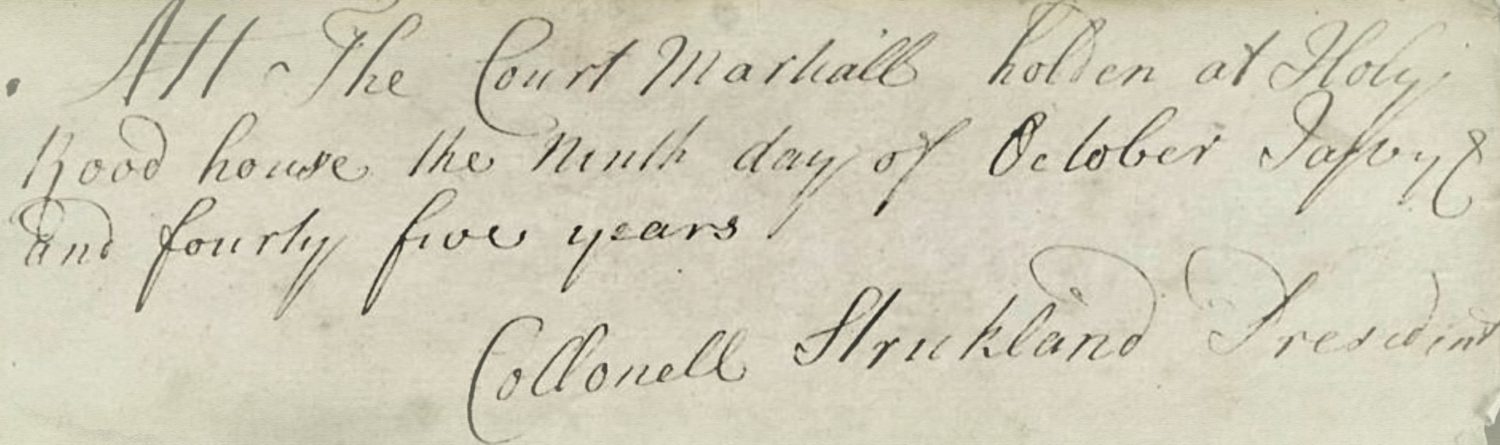After a handful of Donald Cameron of Lochiel’s men slipped through Edinburgh’s grand, turreted Netherbow Port virtually unopposed, the capital of Scotland, excepting its imposing castle, was firmly in Jacobite control for most of the late summer and autumn of 1745. From 17 September to 31 October, high-ranking soldiers and officials under the leadership of Charles Edward Stuart consolidated their provisional government in ‘North Britain’ at Holyrood House, and in the fields around Duddingston Village they bolstered both the numbers and training of the men who formed the military arm of the Jacobite cause. This distinctly irregular army was essentially the crowbar with which Charles Edward would attempt to pry George II off the thrones of the Three Kingdoms while advocating for his father, James Francis Edward, who was proclaimed at the mercat cross as James VIII of Scotland on the very same day the burgh was taken. Cobbled together in fits and starts before the capture of Edinburgh, it was never a sure thing that enough support would materialise or that the enthusiasm it bore would translate to success on the battlefield when open conflict eventually came.1
The lightning-quick and overwhelming Jacobite victory at Prestonpans in the early morning of 21 September boosted the confidence not only of Charles Edward’s Council of War but also that of many of the common soldiers across the ranks. Now that this army had faced seemingly the best that the British government had to offer, the zeitgeist of the mission was astir and word quickly spread to the surrounding localities that this revolution, long-desired and attempted on numerous occasions before, might really happen this time. Recruiting drives marshalled in places like Perthshire and the north-eastern counties, like Aberdeenshire and Forfarshire, eventually secured valuable additions to the nucleus of Highland Jacobite troops in Edinburgh, with numbers swelling from around 2500 to nearly 6000 men through the month of October.2